One of the first rules of trading on the Forex market that is instilled in a trader is the mandatory placement of a stop-loss order to limit potential losses if the price moves against the opened trade. There is no doubt that one of the most important qualities of a trader is the ability to manage losses—this is the direct purpose of the StopLoss order.




- What is a stop-loss
- What is a stop-loss order for
- How does stop-loss work
- How to set a StopLoss order in MetaTrader 4 terminal
- Technical rules for placing a stop-loss order
- How to correctly calculate the size of a stop-loss order
- What is breakeven and how to use it
- What is a trailing stop-loss
StopLoss — this is …
Stop-loss (Stop Loss) is a type of stop order placed by a trader to limit potential losses when the market moves against the opened trade.

What is StopLoss for?
The StopLoss order is an essential element of capital management rules on Forex and allows closing a losing position with a pre-planned loss if the price reverses against the trade, enabling the trader to manage trading risks.
On modern turbulent markets, trading without a stop-loss is unthinkable. When a colleague loudly declares that they never use stop-losses (claiming that a combination of various exits gives them a significant advantage and allows trading without stop-loss orders), professionals understand that their ruin is only a matter of time.
The inevitability of such an outcome is often predetermined by past years when an unprotected position inevitably encounters a strong price drawdown or spike in the opposite direction, measured in tens of figures. In such cases, even the strongest deposit can turn into “dust” with a zero balance.
Trading without stop-loss orders is more common among amateurs. For professionals, the top priority is protecting trading capital from ruin—everything else (profit or loss amounts) is secondary.
How does stop-loss work?
A stop-loss automatically closes the placed position upon reaching the specified price level. The order is stored on the broker’s server, so there is no need to keep the terminal running for it to trigger.
The StopLoss order can close the trade either for the full volume at once or for 1 contract (lot). The opposite order, whose main purpose is to fix profits from the trade, is Take Profit.
Stop-loss can be set for any type of orders, including pending orders.
How to set a StopLoss order in MetaTrader 4 terminal?
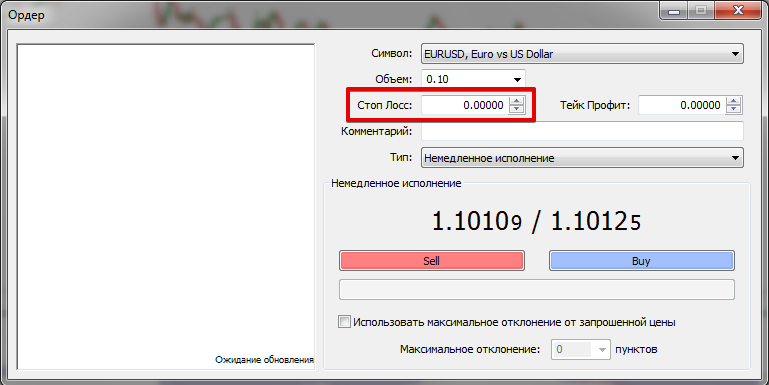
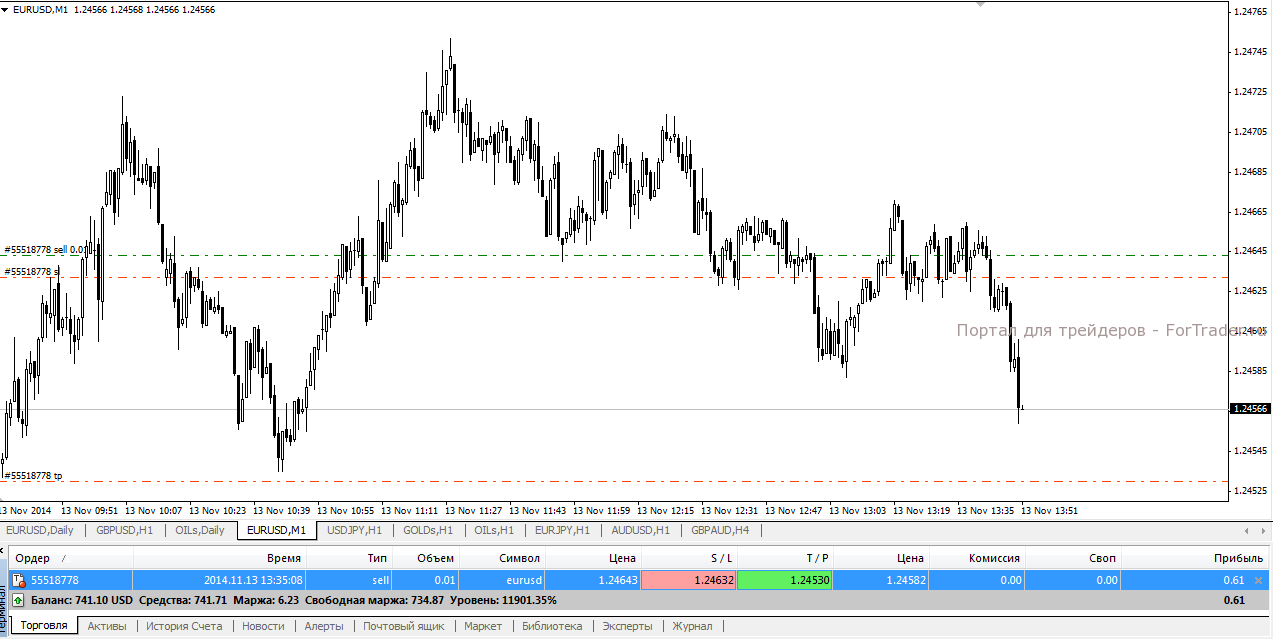
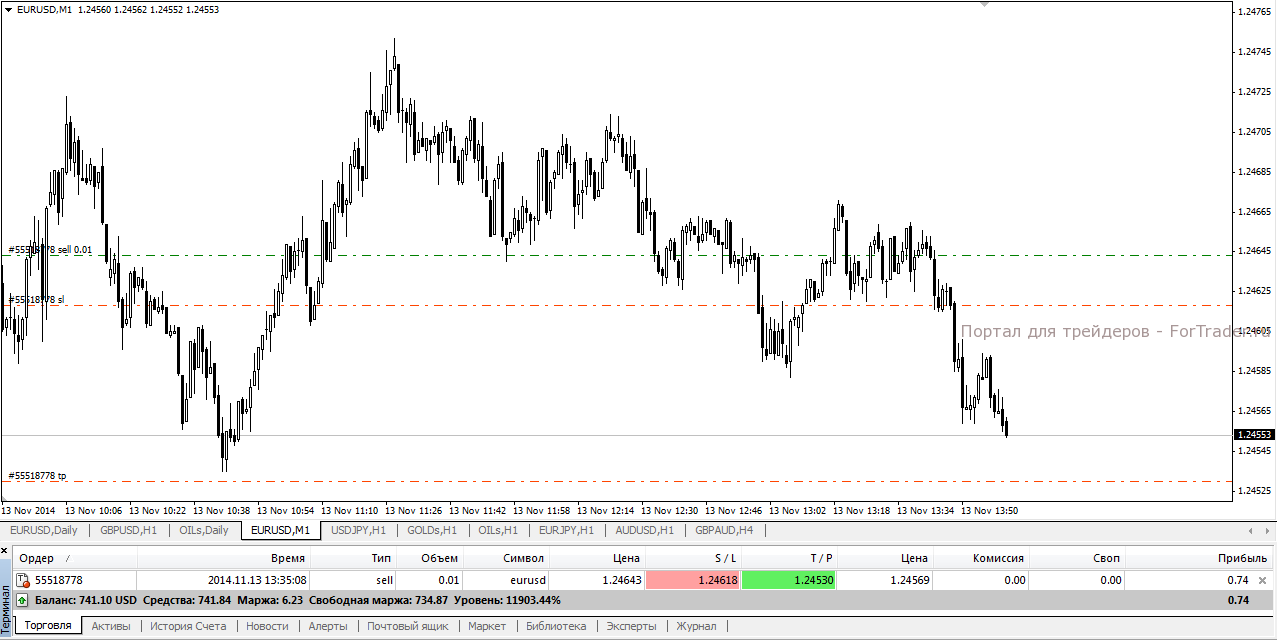
To set a stop-loss order in the MetaTrader 4 terminal when opening a position, enter the required trigger price value in the Order Panel.

For an open trade, the StopLoss value can be modified via the “Modify/Delete Order” tab.
Stop-loss for a buy trade is set below the position, for a sell trade—above the position.
Technical rules for placing stop-loss
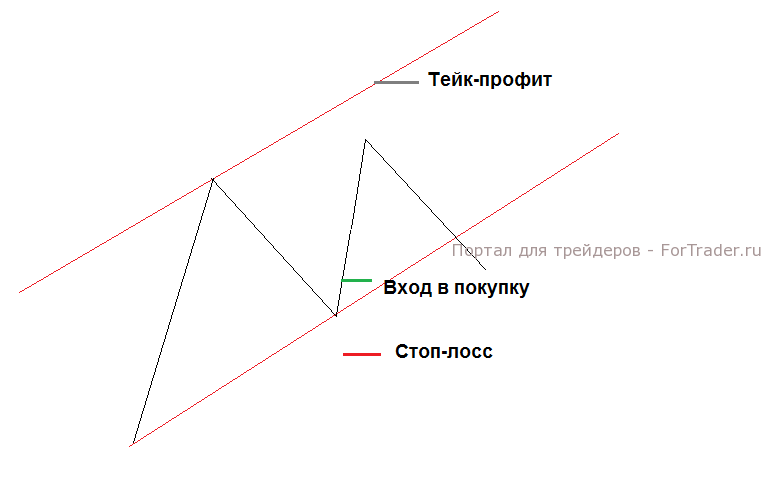
From a technical perspective, placing a stop-loss order depends on strong support and resistance levels. In trend trading, these are trend lines; in flat trading—the flat boundaries.
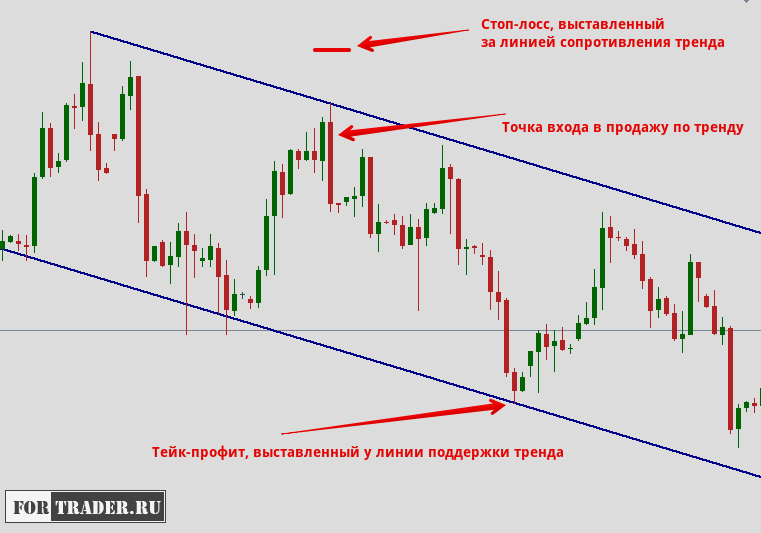
The logic is simple. A strong support or resistance level is unlikely to be broken on the first try, with a high probability of a bounce. Therefore, the stop-loss is placed beyond such a level, typically at the previous high (low). If the support (resistance) level is broken, there is no longer any talk of continuing the trend on which the trade was opened.
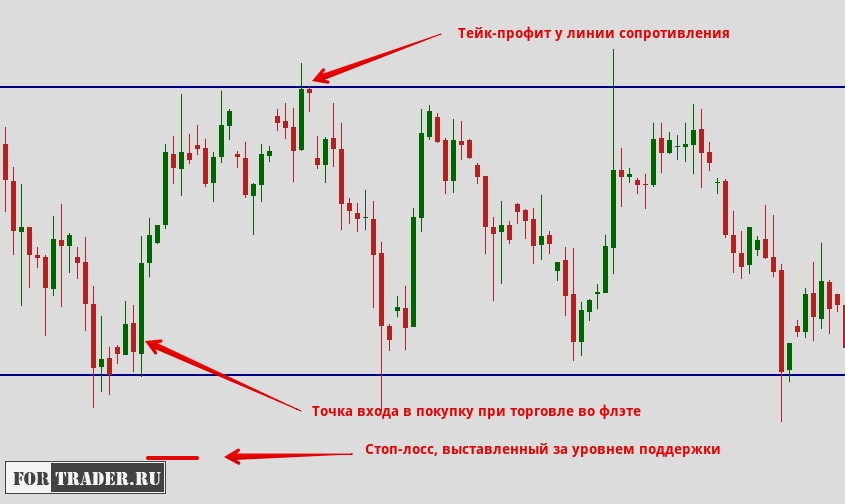
The same principle for placing stop-loss orders is used in all types of trading. Strong support and resistance levels can be identified manually (previous local lows and highs) or using technical level indicators.
When placing a stop-loss, there are several important points:
- First, understand that many market participants place stop-losses beyond key levels. The older the timeframe, the stronger the level and the higher the likelihood of stop-loss clusters nearby, increasing the chance of your order being triggered.
- Do not place stop-loss on “round” levels like 100, 750, etc. These levels psychologically attract most traders.
Rules for calculating stop-loss
Having determined the technical rules for placing a stop-loss order, we can move to the calculation aspect, recalling money management rules, which should never be forgotten.
Essentially, the stop-loss size reflects the amount a trader is willing to risk on the opened trade. Entering the market “all-in,” the risk is naturally 100%. Ideally, the recommended risk level should be 2-5% of the deposit per trade.
For example, a trader’s deposit is $5000. The trader has set a maximum risk of 5%. Accordingly, the loss per trade should not exceed 5000 x 0.05 = $250.
Next, assess the relationship between the stop-loss size, the cost per pip, and the position volume. The trader calculated that at the entry point, the stop-loss will be 50 pips away. The pip cost is 250:50 = $5. Considering that for 1 standard lot, 1 pip costs $10, the recommended position volume is 0.5 lots.
The above example is optimal and does not account for the psychological factor of greed. Unfortunately, many traders, chasing profits, trade a full lot on a $1000 deposit. Accordingly, there is no talk of risk management or calculations.
When setting stop-loss and take-profit orders, remember one very important detail—spread.
For example, a long position in EUR/USD is opened with stop-loss at 1.1150 and take-profit at 1.1230. The spread is 2 pips. Accordingly, take-profit will trigger at 1.1232, and stop-loss at 1.1152.
The example is for a fixed spread. For floating spread accounts, it’s more complex, as during major economic data releases or events, the floating spread can increase several times.
For more details on how to correctly calculate a stop-loss order, watch the webinar by renowned trader Alexander Gerchik:
What is breakeven?
Breakeven (breakeven level, BE) is moving the StopLoss order in an open trade to the entry price level after the price has moved a certain number of pips in the desired direction.<