Fibonacci
Fibonacci extensions are a tool that displays horizontal lines based on Fibonacci numbers. These lines can be used as key support and resistance levels.
To use this tool, first identify the minimum and maximum points on the chart, then draw it from the minimum to the maximum.
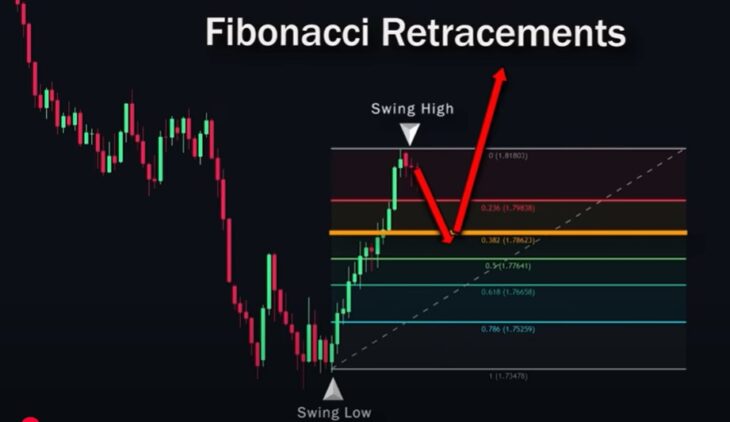
Next, wait for the price to retrace to one of these levels, preferably the 0.382 level, as this is the most common level from which price usually reverses.
If the price reaches this value, it may be a good entry point for buying. Keep in mind that price can also reverse from other Fibonacci levels, so it’s better to combine the indicator with other confirming signals for more accurate entries.
Breakout Patterns
Breakout patterns are sharp and significant price movements in one direction, usually occurring after a consolidation period. For example, price consolidates and then suddenly moves sharply downward. This is called a breakout.
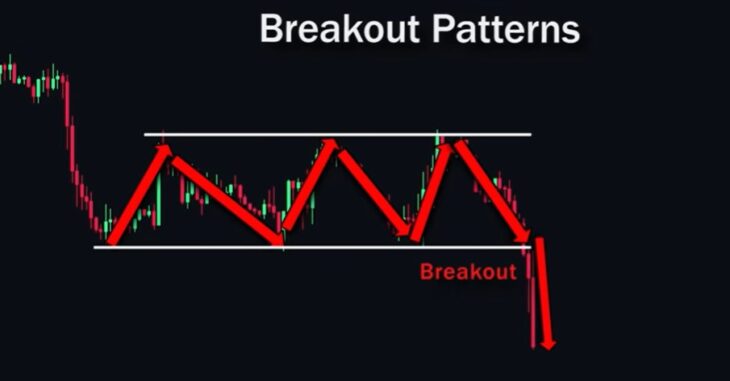
To take advantage of this movement, traders can use certain patterns to identify breakouts before they occur. The most well-known breakout patterns are wedges, triangles, and rectangles.
Reversal Patterns
Reversal patterns occur when price moves in the opposite direction of the current trend, forming countertrend movements. Certain patterns on the chart can help traders predict reversals before they appear.
The most well-known reversal patterns:
- Double top and double bottom
- Triple top and triple bottom
- Head and shoulders
- Cup with handle
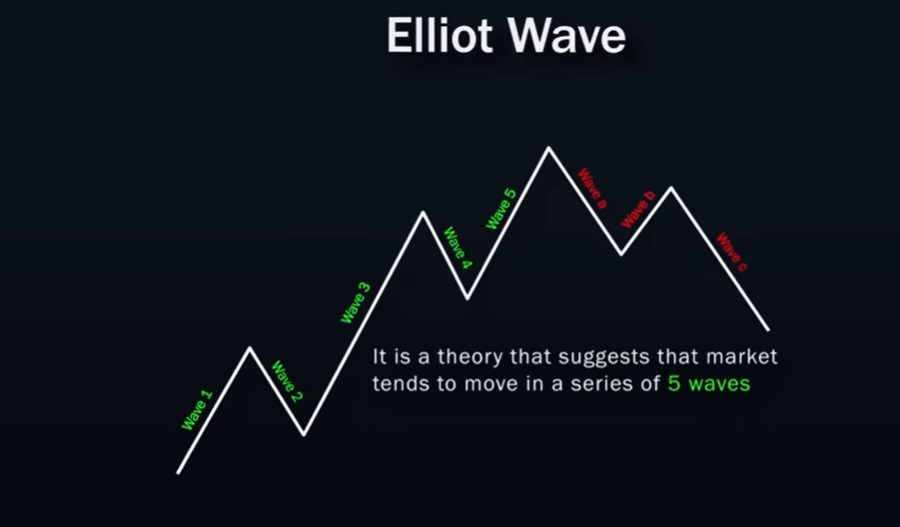
Elliott Waves
The Elliott Wave theory suggests that the market moves in a series of five waves before reversing and forming a new set of waves in the opposite direction. By understanding the sequence of Elliott Waves, traders can predict future price movements. On the chart, wave points can be marked as 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, and then corrective waves as A, B, C.
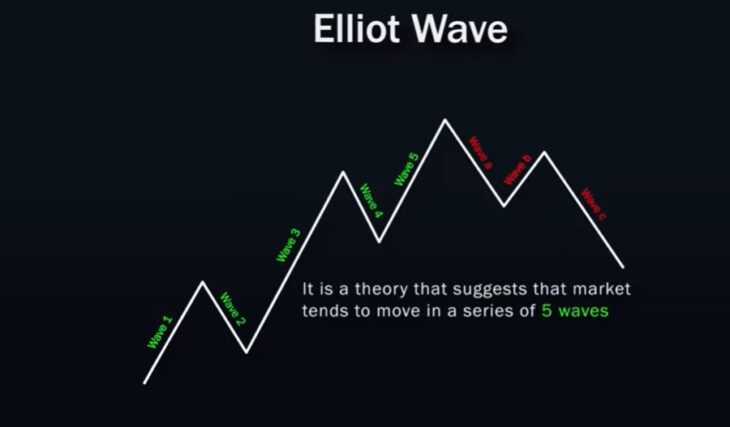
There are strict rules for a movement to be considered valid according to Elliott Wave theory:
- Wave 2 cannot be longer than wave 1 and usually retraces to the 0.618 Fibonacci level.
- Wave 3 must be the longest among waves 1, 3, and 5.
- Wave 4 must remain above the peak of wave 1 and usually retraces to the 0.382 Fibonacci level.
Example of application: if wave 4 retraces to the 0.382 Fibonacci level before continuing upward, this may be a potential entry point for buying.
Fair Value Gap
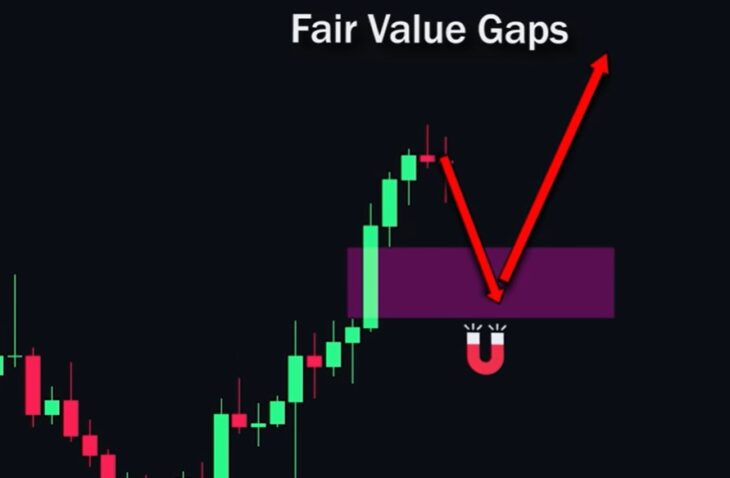
A Fair Value Gap occurs when a candle forms a significant gap due to an imbalance between buying and selling. To find such a gap, first locate a candle with a large body, then draw a rectangle on the gap between the tail of the previous candle and the tail of the next candle. This level can now act as a “magnet” to which price may return before continuing its movement.
Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns help traders analyze future price movements based on candle shapes.
The most well-known candlestick patterns:
- Engulfing pattern — indicates strong momentum in the direction of the engulfing candle.
- Hammer and shooting star — signal price rejection, visible by a long tail.
- Doji — signals market uncertainty.
Heikin Ashi
The Heikin Ashi indicator replaces traditional candles with a smoother chart.
- A green Heikin Ashi candle signals an uptrend.
- A red Heikin Ashi candle signals a downtrend.
- The larger the candle body, the stronger the trend.
However, this indicator is used only for analysis and does not display the actual market price.

Lunar Phases
A concept that uses lunar cycles to determine market trends. Some traders believe that lunar cycles correlate with human emotions and behavior, which can affect the market:
- New moon is associated with a bullish market.
- Full moon is associated with a bearish market.
These days, this method is mainly used as an additional confirmation tool.
Renko Charts
Renko charts replace standard candlestick charts, using blocks instead of candles. Unlike traditional candles, where a new candle forms by time, Renko charts form only when price changes by a set percentage or amount.
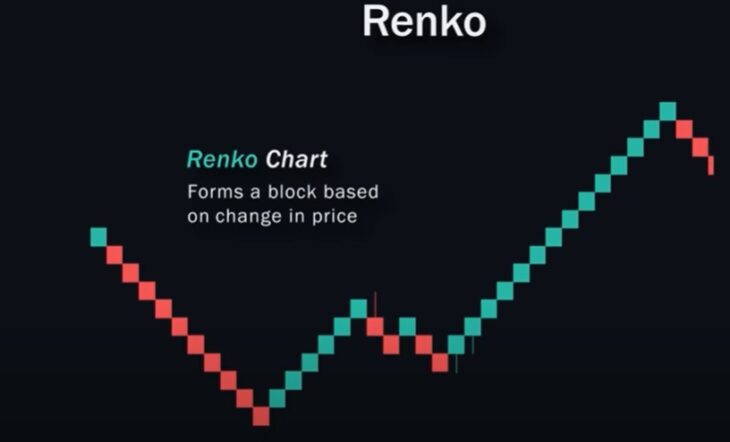
- A green Renko block indicates an uptrend.
- A red Renko block indicates a downtrend.
This tool helps filter out market noise.
Harmonic Patterns
Advanced price movement patterns based on Fibonacci numbers.
Examples:
- Bat — forms when price movement resembles the letter “M”
- Butterfly
- Crab
These patterns are used to forecast future price movements.
Support and Resistance
Key horizontal levels where price has bounced in the past and may bounce again:
- If the level is below the current price, it is support, where buying can be considered.
- If the level is above the current price, it is resistance, where selling can be considered.
Dynamic Support and Resistance
Differs from standard support and resistance in that it uses not static lines, but indicators, such as moving averages.
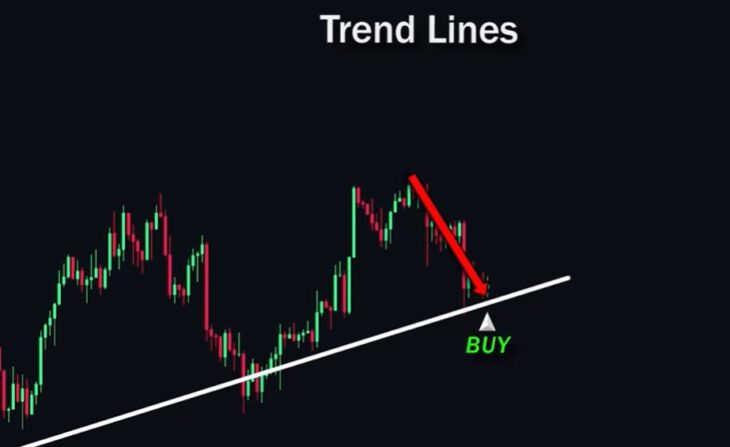
Trend Lines
Diagonal levels that help determine the overall market direction:
- An ascending trend line indicates a bullish market.
- A descending trend line indicates a bearish market.
Price retesting a trend line may be a good entry point.
Gann Fan
A tool that displays lines at different angles, which can act as key support and resistance levels.
Trend Indicators
Examples of trend indicators:
- MACD — line crossovers indicate trend changes.
- Moving averages — price above average → bullish trend, below → bearish trend.
- Parabolic SAR — dots below price → uptrend, dots above price → downtrend.
Oscillators
Oscillators are indicators that display the relative strength of price. They are especially effective in sideways (flat) markets, where there is no clear trend. The most popular ones include:
- RSI (Relative Strength Index)
When the RSI line is in the oversold zone, it may signal a possible upward reversal.
When the line is in the overbought zone, it indicates a likely reversal downward. - Stochastic Oscillator
If both oscillator lines are in the oversold zone, it may indicate a reversal upward.
If they are in the overbought zone, a reversal downward is likely.
Additionally, crossovers of the stochastic lines can signal future price movements.
Divergences
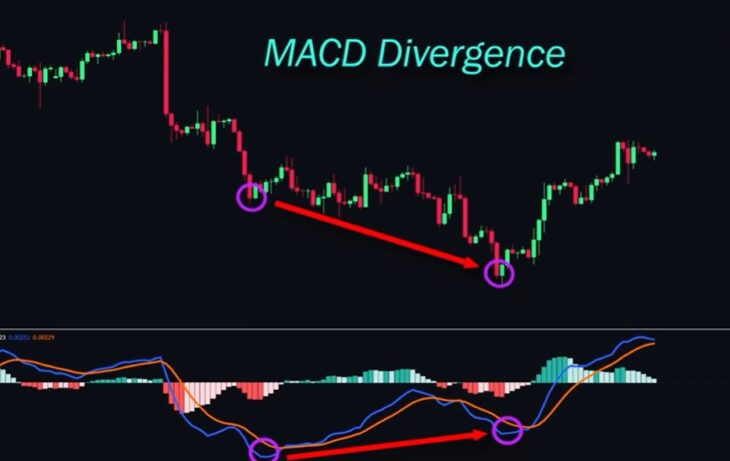
Divergence occurs when the indicator moves in the opposite direction of the actual price movement. This usually signals a possible trend change.
Divergence can be observed on various indicators, such as MACD, Stochastic, and RSI.
For example, if using the MACD indicator, price forms higher highs (uptrend), but the indicator shows lower highs (bearish signal), this is called bearish divergence and may indicate an upcoming downward reversal.
Volume Indicators
Volume indicators help determine the strength of price movement by tracking trading volume. These include:
- Price Volume
The length of the bars on the histogram shows trading volume. The longer the bar, the higher the volume. - Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP)
This indicator shows the average price of an asset, weighted by volume. It can be used as dynamic support and resistance. - Volume Profile
Displays trading volume horizontally, helping identify key levels where price may meet support or resistance.
Demand and Supply Zones (Order Blocks)
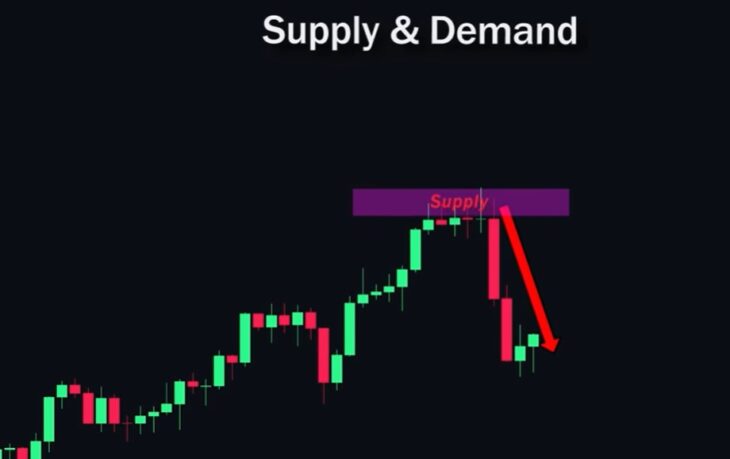
Demand and supply zones are areas where significant price movements occurred.
- Demand Zone forms if price sharply rose from a certain level. This can be a good point for buying.
- Supply Zone forms if price sharply fell from a certain level. This can be a good point for selling.
Similar to support and resistance levels, these zones can serve as key entry points for trades.
Market Structure
Market structure analyzes price behavior, condition, and dynamics.
- An uptrend structure is defined by a sequence of higher highs and higher lows.
- A downtrend structure is characterized by lower highs and lower lows.
Break of Structure (BOS)
Occurs when price breaks the previous high or low within a trend. For example, if price sequentially forms higher highs and lows, breaking the previous high is considered a break of structure.
Change of Character (CHoCH)
Happens when price breaks the previous trend structure, signaling a possible reversal. For example, if price forms a sequence of higher highs and lows, but then breaks the previous low and starts forming lower lows, this indicates a change of character.
These are the main concepts that help analyze the market and build trading strategies. A more detailed Forex video with examples of these Forex strategies:
* To translate, enable subtitles in the settings and set their translation to your desired language.