Blockchain technology was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto. When you hear the word “blockchain,” you often think of Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies, and complex technical systems. However, the essence of the technology is much broader—and simpler—than it seems. It is a method of storing information in a way that makes it impossible to falsify, erase, or lose.
This technology is already transforming not only finance but also healthcare, logistics, government services, and even art. At the core of blockchain lies a simple yet brilliant idea: to link data into a “chain” of blocks that cannot be altered retroactively. This creates a system where trust is based not on people but on mathematics. In this article, we will explore what blockchain is, how it works, and why it is considered one of the most important technologies of the 21st century.
Contents
- The Essence of Blockchain Technology
- How Blockchain Works
- What Makes Blockchain Different
- Features of the Blockchain Network
- What Are Cryptographic Keys
- Participants in the Blockchain System
- Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Future Prospects of Blockchain Technology
The Essence of Blockchain Technology
Blockchain (chain of blocks) is an English term formed from the words block and chain, meaning a chain of blocks. Simply put, blockchain is a database made up of blocks.
The key feature that sets blockchain apart from other systems is that the information stored is decentralized. In simple terms, this means there is no single set of servers storing the data—instead, all data is distributed among the participants of the system without exception.
Bitcoin and all other cryptocurrencies are built on blockchain technology. However, blockchain can be used beyond financial transactions. The blocks that make up the blockchain can store any information traditionally kept on paper: credit histories, traffic violations, property rights—anything at all!
Main features of blockchain:
- Transparency: all network participants can view the records in the blockchain.
- Immutability: it is practically impossible to alter data retroactively without changing all subsequent blocks.
- No central authority: data is not stored on a single server but on thousands of computers worldwide (decentralization).
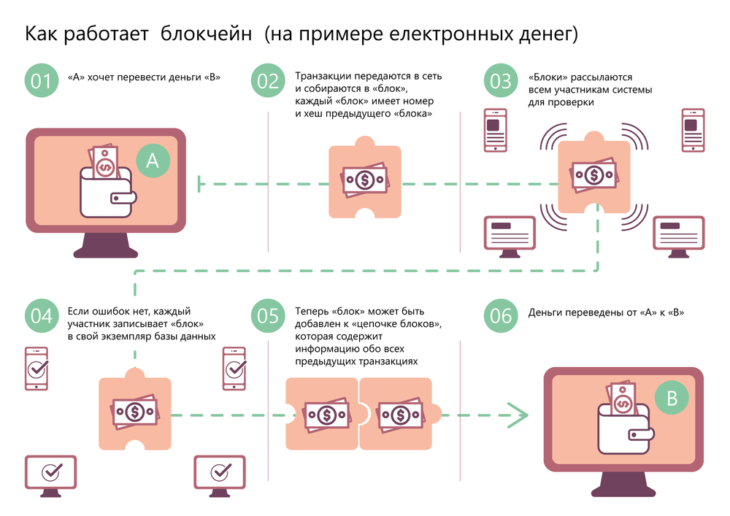
How Blockchain Works
In fact, the principle behind blockchain technology is not complicated. Imagine a large ledger book recording financial transactions of money coming in and going out.
Each page of this book is a block of information, and the entire book is the blockchain—a chain of blocks. But unlike a traditional ledger, this “book” is not kept by a single accountant; instead, it exists simultaneously on every user’s computer in the system.
Each block in the system contains a reference to the previous block, so if someone tries to change or remove a block from the chain, the system immediately detects the inconsistency because it constantly compares with hundreds of thousands of identical “books.”
The closest analogy to blockchain is the Torrent network, which operates on a P2P (peer-to-peer) principle—where all participants have equal rights. For example, information in the Torrent network is not stored on a central server. When downloading a movie (legally, of course), you get it directly from other participants in the network. The information “lives” as long as at least one participant remains online.
Blockchain works the same way. Participants request information directly from each other.
What Makes Blockchain Different
How do blocks link into a chain? This is done through encryption based on complex mathematical algorithms, also known as hashing.
Hashing is performed by computers within the network. Simply put, network computers solve a mathematical problem. Once they reach the same solution, a new data block is created.
This block is assigned a timestamp, which is its hash sum. Just as no two people have identical fingerprints, each block has a unique hash sum.
After the ledger is updated, the created block cannot be changed—only new information can be added to it. The ledger updates simultaneously on all computers in the network. Any attempt to manually alter the block sequence will be rejected by the blockchain system due to hash sum mismatches.
Features of the Blockchain Network
As mentioned earlier, blockchain is a peer-to-peer network. The more participants in the system, the stronger and more stable it becomes. All users have equal rights—there is no administrative authority.
Information stored on the blockchain is accessible to anyone.
You can open any block in the chain to study it. Blockchain allows tracking all changes made to the information and verifying its accuracy. Therefore, fraud or manipulation in the blockchain system is fundamentally impossible.
Despite the openness of blockchain data, it is securely protected.
In other words, the information provided by a blockchain block can reveal all millionaires. It can reveal them, but not identify who they are. Identification requires a special key that the system uses to recognize the user.
What Are Cryptographic Keys
The keys mentioned above simplify the process of verifying the truthfulness and accuracy of data. A cryptographic key is a group of numbers and letters generated by a hash function. Cryptographic keys in the blockchain network have two main features:
- Having the key does not allow you to know the original (primary) information;
- It is impossible to create a data package that would generate an already existing key.
Simply put, possessing a cryptographic key cannot harm an individual user or the system as a whole. However, the available data can be used to verify the correspondence of information to a specific key.
Cryptographic keys are exactly what link blocks into a chain. Besides the current block’s key, it also encrypts the keys of previous blocks. Any attempt to change the information in a block will alter the block’s key, which the system will immediately detect. Moreover, the block’s key guarantees network security, which grows proportionally with the network’s expansion.
Participants in the Blockchain System
Anyone with a computer can become a participant in the blockchain system. All users have equal rights. The system is structured around two groups of participants:
- Regular participants – users who create records in blocks. They receive ready-made blocks stored on their computers to verify both their own and others’ data.
- Miners – people who create new blocks using their computing power. Miners collect records from regular users, form them into blocks, and distribute them across the network.
Until a record is added to a block, it is considered invalid and requires confirmation. If you have used a Bitcoin wallet, you have probably seen a message that a transaction will be completed after several confirmations. Once a record is confirmed and written into a block, it cannot be changed in any way.
 Blockchain Technology.
Blockchain Technology.
Advantages of Blockchain Technology
- Direct data exchange between network participants, eliminating intermediaries.
- Blockchain is nearly impossible to hack—it would require access to all computers in the network.
- Reliability increases with the number of users in the system.
- Personal data security—hashing is irreversible.
The impossibility of altering or falsifying data recorded in blocks is ensured because any change would alter the cryptographic key, which the system would immediately detect.
Future Prospects of Blockchain Technology
Initially, blockchain technology was the foundation for the Bitcoin cryptocurrency. However, over time, its applications have expanded. Any industry with databases can be transitioned to blockchain technology.
In the blockchain system concept, it is impossible not to mention smart contracts, which act as a form of “enforced honesty,” freeing users from legal red tape. For example, the electronic notary Stampery uses blockchain technology to certify transactions.
Overall, blockchain technology can be applied almost everywhere, and it is likely that more and more companies and organizations will adopt blockchain over time.
Considering the growing number of blockchain users and its current scale of application, it is simply impossible to ignore this technology.











